Environmental Effect
The formation of nitrogen oxide
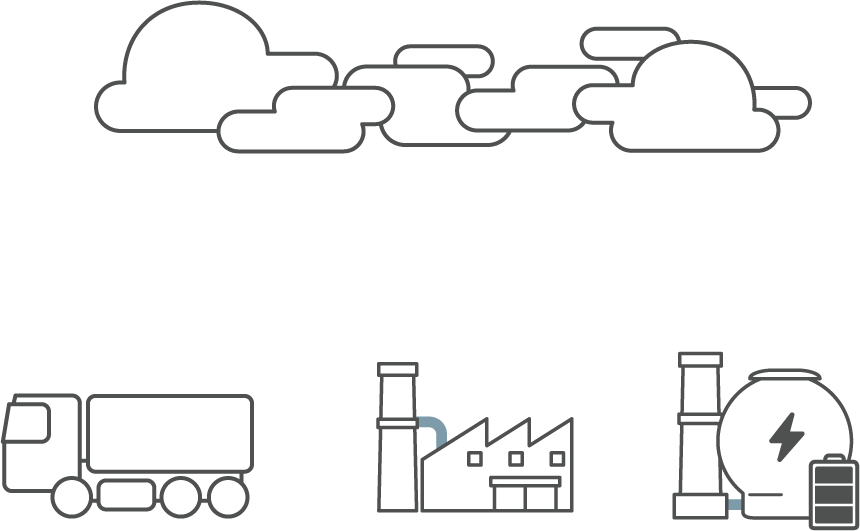
Nitrogen oxide (NOx) is a chemical compound combined with nitrogen and oxygen.
There is 78% of nitrogen in the atmosphere and it usually does not combine with oxygen but in the circumstances of high temperature, it combines with oxygen and thus results in nitrogen oxide (NOx).
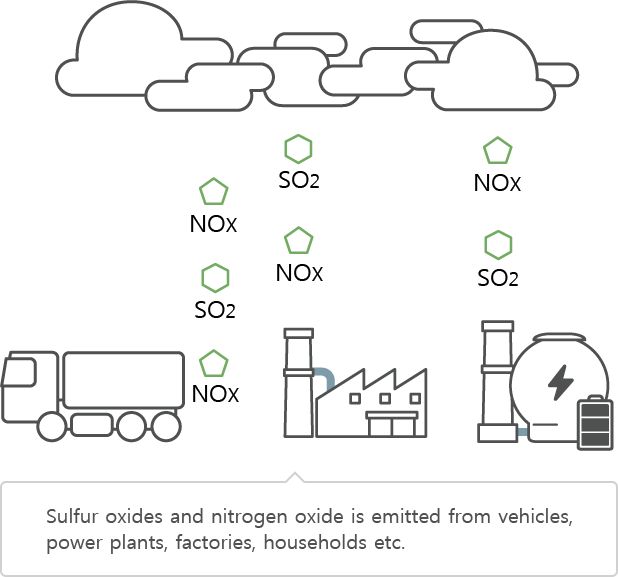
Nitrogen oxide results from nitrogen and oxygen combination from high temperature equipment such as boilers, blast furnace, incineration plants, vehicle engines, etc.

Nitrogen acid turn into acid rain
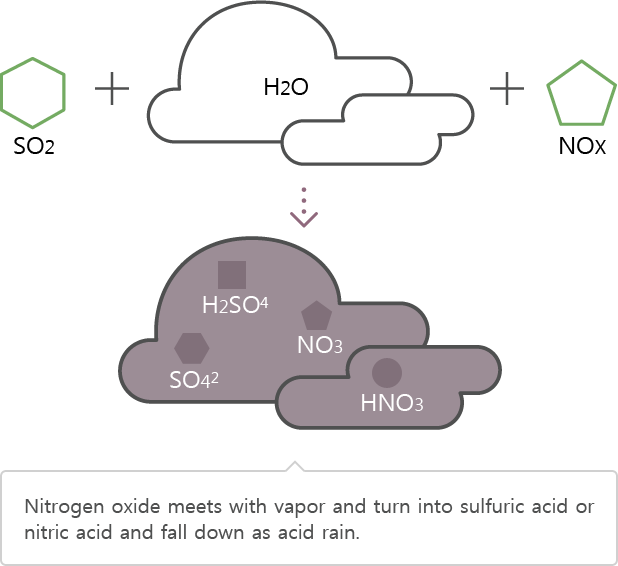
Nitrogen oxide resulting from factories oxidizes through water vapor in the atmosphere and transforms into sulfuric acid or nitric acid that exerts negative effects to the human body.
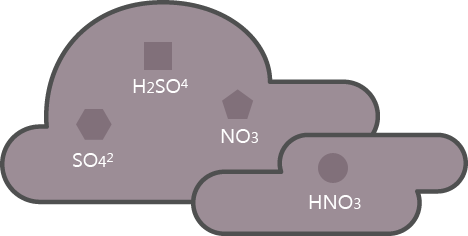
SO2 → SO42, H2SO4
NOx → NO3, HNO3
Nitric acid or sulfuric acid falls from the atmosphere through absorption to rain, snow, and mist.

Harmful effects from acid rain

Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a cause for pulmonary emphysema or bronchitis, and through the hydrocarbon in the atmosphere and sunlight, it can produce photochemical smog of ozone (O3), formaldehyde (HCHO) and affect human body through the eyes or noses.
Nitrogen monoxide (N2O) causes greenhouse gas in the dissolution process of microorganisms, and by reacting to water, it becomes nitric acid (HNO3) and can cause the depletion of the ozone layer and acid rain.
Acid rain can cause significant harmful effects to the environment. Fish, which are vulnerable to acid, will be harmed first, and then the soil will become contaminated and will result in harming plants growing from the soil and human bodies ingesting these plants.
